Each nephron is made up of two major parts:
We tackled renal corpuscle in the previous article, this article will be dedicated to the second part of nephron which is:
The Renal tubule is a long, complicated tubule, about 15 mm long and 55 μm in diameter. The tubular portion of the nephron is the continuation of the Bowman capsule.
The proximal convoluted tubule is the coiled part of the Bowman capsule. It's situated in the cortex. It continues as the descending limb of Henle's loop. The length of the proximal convoluted tubule is 14 mm and the diameter is 55 μ.
The proximal convoluted tubule is formed by a single layer of cuboid epithelial cells. The characteristic feature of these cells is the presence of hair-like projections directed towards the lumen of the tubule. Because of the presence of these projections, epithelial cells are called brush-bordered cells.
The fluid flows from the proximal tubule to the loop of Henle (or the loop of the nephron) which dips into the renal medulla.
Each loop consists of a descending limb and an ascending limb. The walls of the descending limb and the lower end of the ascending limb are very thin and are thus called the thin segment of the Henle loop. After the ascending limb of the loop returns partway back to the cortex, the surface becomes much thicker and is referred to as the thick segment of the ascending limb.
At the end of the thick ascending limb, there is a short segment with a plaque of specialized epithelial cells in its wall, known as the macula densa., macula densa plays an important role in the regulation of nephron function.
The distal convoluted tubule is a continuation of the thick ascending segment and, like the proximal tubule, is located in the renal cortex. The length of the distal convoluted tubule is 14.5 to 15 mm. It is from 22 to 50 μ in diameter.
The distal convoluted tubule is lined with a single layer of cuboid epithelial cells without a brush border. The epithelial cells in the distal convoluted tubule are called intercalated cells (I cell). beyond the macula densa, the fluid reaches the distal tubule, followed by the connecting tubule and the cortical collecting tubule, which lead to the cortical collecting duct.
Initial sections of 8 to 10 cortical collecting ducts are joined together to create a single larger collecting duct, which runs down into the medulla and becomes a medullary collecting duct.
Collecting ducts merge into progressively larger ducts that are eventually drained into the renal pelvis via the tips of the renal papillae. There are about 250 of the very large collecting ducts in each kidney, each of which collects urine from about 4000 nephrons.
1. GUYTON AND HALL, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12th edition, Jackson, Mississippi, University of Mississippi Medical Center, [2011]
2. K SEMBULINGAM AND PREMA SEMBULINGAM, Essentials of Medical Physiology, Sixth Edition, New Delhi, Panama City, London, Dhaka, Kathmandu, JAYPEE BROTHERS MEDICAL PUBLISHERS (P) LTD, [2012]
3. INDU KHURANA AND ARUSHI KHURANA, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 2nd Edition, India, Elsevier India, [December 1, 2015]
4. JOHN FEEHALLY, JÜRGEN FLOEGE, MARCELLO TONELLI, RICHARD J. JOHNSON, Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, Sixth Edition, Edinburgh, London, New York, Oxford, Philadelphia, StLouis, Sydney, Elsevier, [September 11, 2018]
5. VALERIE C. SCANLON, TINA SANDERS, Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, fifth edition, New York, F. A. Davis Company, [January 1, 2006]
6. KIM E. BARRETT, SUSAN M. BARMAN, HEDDWEN L. BROOKS, JASON YUAN, Ganong's Review of Medical Physiology, 26th edition, New York, Chicago, San Francisco, Athens, London, Madrid, Mexico City, Milan, New Delhi, Singapore, Sydney, Toronto, Mc Graw Hill Education, [January 29, 2019]
7. ANNE WAUGH, ALLISON GRANT, Ross and Wilson ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY in Health and Illness, 11th edition, Edinburgh, London, New York, Oxford, Philadelphia, St Louis Sydney, Toronto, Churchill Livingstone, [September 7, 2010]
The renal corpuscle is formed by two parts: 1. Glomerulus 2. Bowman capsule (glomerular capsule), Glomerulus is a tuft of capillaries enclosed by bowman capsule.
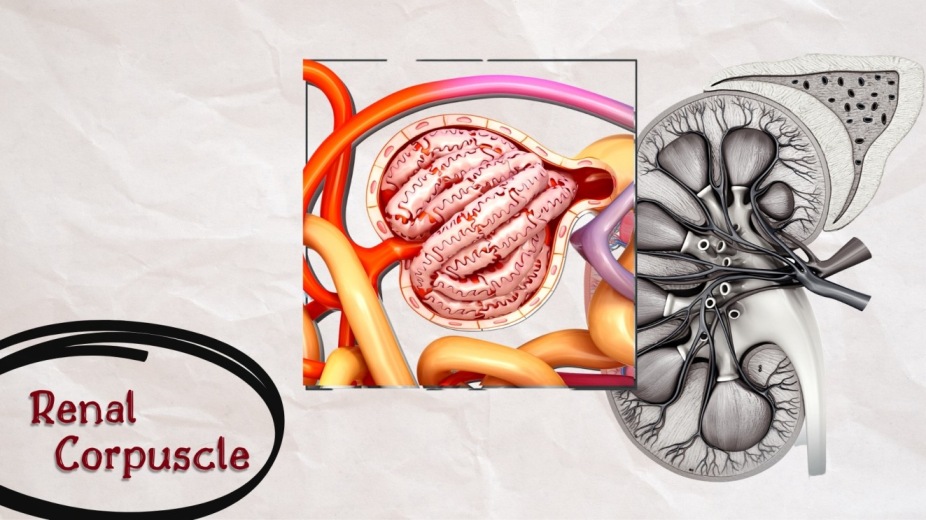
Juxtaglomerular apparatus as indicated by the name (juxta - near) refers to the collection of specialized cells which their primary function is to secrete the hormones.

The urethra is a muscular canal that extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior of body. Read more about the anatomy of urethra in this article.

Dosage guide of Lisinopril: Click to read about the dose for your specific condition and age group.

Learn about medical uses, safety profile, mechanisms and interactions of statins.

Comprehensive guide on Ozempic (semaglutide), including its uses, dosage, side effects, warnings, and interactions.
.png)