Each nephron is made up of two major parts:
Renal corpuscle (Malpighian corpuscle) is a spheroidal and slightly flattened structure with a diameter of about 200 μ. The renal corpuscle is located in the cortex of the kidney, either near the periphery or near the medulla. The function of the renal corpuscle is the filtration of the blood that forms the first phase of urine formation.
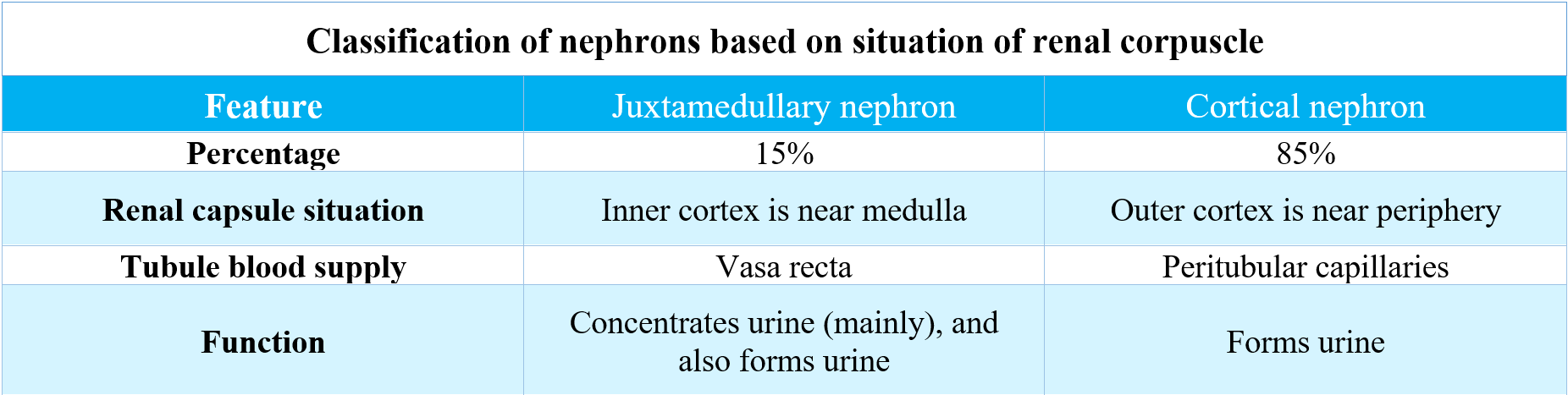
Based on the situation of the renal corpuscle, nephrons are classified into two types:
The renal corpuscle is formed by two parts:
Glomerulus is a tuft of capillaries formed by an afferent arteriole and drained into an efferent arteriole enclosed by the Bowman capsule. Blood reaches the glomerulus through an afferent arteriole and exits it through an efferent arteriole (note that the efferent vessel is an arteriole and not a venule).
Afferent and efferent arterioles lie close together at a point referred to as the vascular pole of the renal corpuscle. The diameter of the efferent arteriole is smaller than that of the afferent arteriole, which helps to maintain comparatively high blood pressure in the glomerulus.
The glomerular capillaries consist of a single layer of endothelial cells connected to the basement membrane. The endothelium has several pores called fenestrae or (filtration pores). Each pore has a diameter of 0.1 μ. The existence of the fenestrae is evidence of the filtration function of the glomerulus.
Bowman's capsule (or glomerular capsule) is the extended end of the renal tubule; it encloses the glomerulus and consists of two layers: the inner layer of the glomerular capsule is called the visceral layer, and the outer layer is called the parietal layer.
The two layers of the Bowman capsule are composed of a single layer of flattened epithelial cells resting on the basement membrane. The basement membrane of the visceral layer fuse with the basement membrane of the glomerular capillaries on which the capillary endothelial cells are organized.
Thus, the basement membranes, which are fused together, form a distinction between the glomerular capillary endothelium and the visceral layer epithelium of the Bowman capsule. The epithelial cells of the visceral layer fuse with the basement membrane, but the fusion is not complete. Each cell is bound to the basement membrane by cytoplasmic extensions of epithelial cells called pedicles or feet. These pedicles are arranged in an interdigitating manner, leaving narrow cleft-like spaces in between. The cleft-like space is called the slit pore. Pedicle epithelial cells are called podocytes.
The renal corpuscle is composed of Glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule. Glomerular capillaries arise from the afferent arteriole. After entering the Bowman capsule, the afferent arteriole divides into 4 or 5 large capillaries.
1. GUYTON AND HALL, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12th edition, Jackson, Mississippi, University of Mississippi Medical Center, [2011]
2. K SEMBULINGAM AND PREMA SEMBULINGAM, Essentials of Medical Physiology, Sixth Edition, New Delhi, Panama City, London, Dhaka, Kathmandu, JAYPEE BROTHERS MEDICAL PUBLISHERS (P) LTD, [2012]
3. INDU KHURANA AND ARUSHI KHURANA, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 2nd Edition, India, Elsevier India, [December 1, 2015]
4. JOHN FEEHALLY, JÜRGEN FLOEGE, MARCELLO TONELLI, RICHARD J. JOHNSON, Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, Sixth Edition, Edinburgh, London, New York, Oxford, Philadelphia, StLouis, Sydney, Elsevier, [September 11, 2018]
5. VALERIE C. SCANLON, TINA SANDERS, Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, fifth edition, New York, F. A. Davis Company, [January 1, 2006]
6. KIM E. BARRETT, SUSAN M. BARMAN, HEDDWEN L. BROOKS, JASON YUAN, Ganong's Review of Medical Physiology, 26th edition, New York, Chicago, San Francisco, Athens, London, Madrid, Mexico City, Milan, New Delhi, Singapore, Sydney, Toronto, Mc Graw Hill Education, [January 29, 2019]
7. ANNE WAUGH, ALLISON GRANT, Ross and Wilson ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY in Health and Illness, 11th edition, Edinburgh, London, New York, Oxford, Philadelphia, St Louis Sydney, Toronto, Churchill Livingstone, [September 7, 2010]
A nephron is classified as the structural and functional unit of the kidney. The two types of nephrons are� cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons.

The Renal tubule is a long, complicated tubule, about 15 mm long and 55 μm in diameter. The tubular portion of the nephron is the continuation of...

The urethra is a muscular canal that extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior of body. Read more about the anatomy of urethra in this article.

Dosage guide of Lisinopril: Click to read about the dose for your specific condition and age group.

Learn about medical uses, safety profile, mechanisms and interactions of statins.

Comprehensive guide on Ozempic (semaglutide), including its uses, dosage, side effects, warnings, and interactions.
.png)