Juxtaglomerular apparatus or (juxtaglomerular complex) as indicated by the name (juxta — near) refers to the collection of specialized cells located between the distal convoluted tubule and the afferent arteriole.
The primary function of the juxtaglomerular apparatus is to secrete the hormones. It also regulates the glomerular blood flow and the (glomerular filtration rate).
Hormone secretion secretes two hormones:
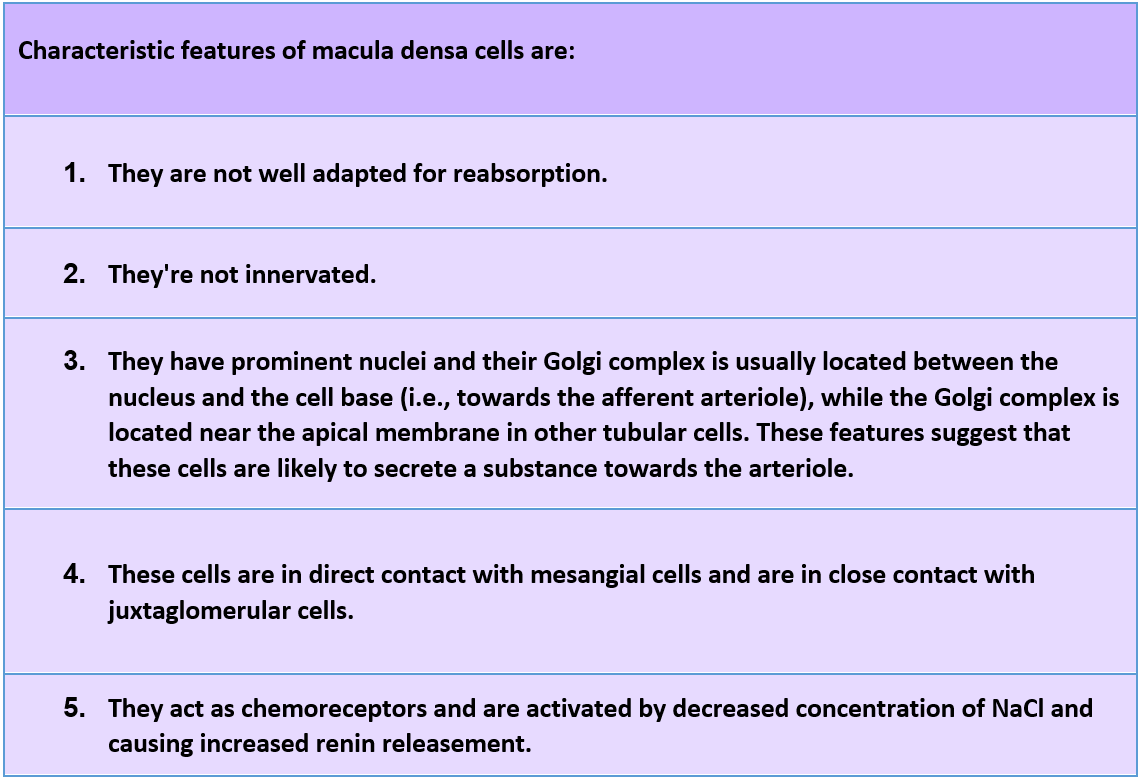
Macula densa is the final component of the thick ascending segment before it opens into a distal convoluted tubule. It is found between the afferent and the efferent arterioles of the same nephron in the wall of the (distal convoluted tubule). It is very close to the afferent arteriole. The macula densa is formed by tightly packed cuboid epithelial cells.
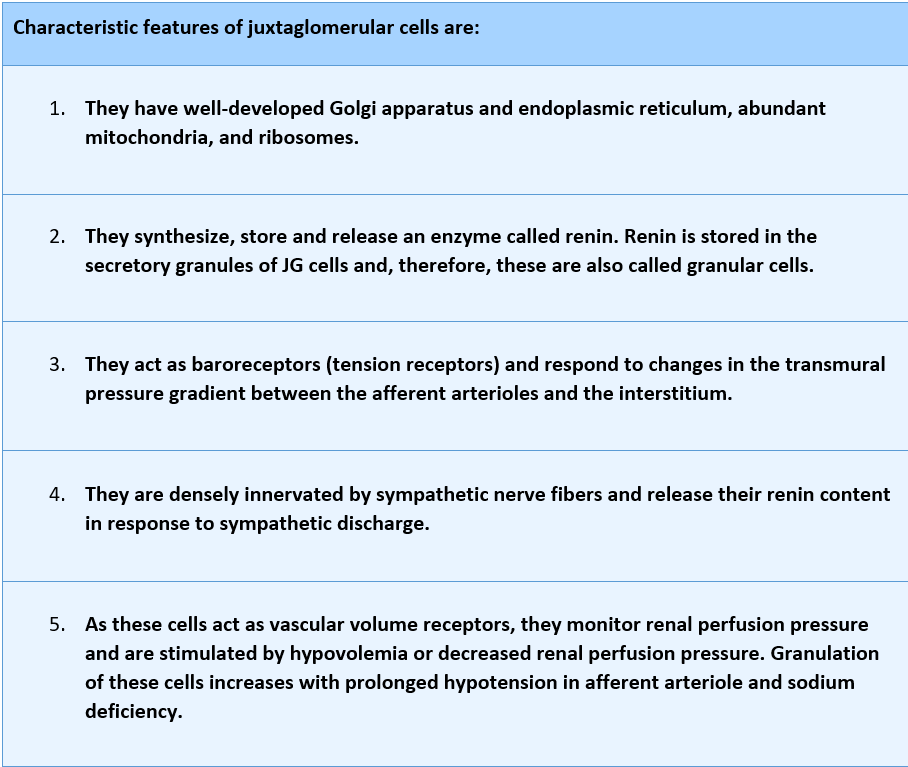
Juxtaglomerular (JG) cells are specialized myoepithelial (modified vascular smooth muscle) cells found in the wall of the afferent arteriole just before entering the Bowman capsule. These smooth muscle cells are mainly present in the tunica media and the tunica adventitia wall of the afferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular cells are also called granular cells because of the presence of secretory granules in their cytoplasm.
Extraglomerular mesangial cells are located in the triangular region bound by afferent arteriole, efferent arteriole, and macula densa. These cells are also referred to as agranular cells, lacis cells, or Goormaghtigh cells.
In addition to extraglomerular mesangial cells, there is another type of mesangial cells located between glomerular capillaries called mesangial glomerular or intraglomerular mesangial cells. Glomerular mesangial cells support glomerular capillary loops by surrounding capillary cells in the form of a cellular network.
These cells play an important role in regulating glomerular filtration by their contractile properties. Glomerular mesangial cells are phagocytic. These cells also secrete glomerular interstitial matrix, prostaglandins, and cytokines.
1. GUYTON AND HALL, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12th edition, Jackson, Mississippi, University of Mississippi Medical Center, [2011]
2. K SEMBULINGAM AND PREMA SEMBULINGAM, Essentials of Medical Physiology, Sixth Edition, New Delhi, Panama City, London, Dhaka, Kathmandu, JAYPEE BROTHERS MEDICAL PUBLISHERS (P) LTD, [2012]
3. INDU KHURANA AND ARUSHI KHURANA, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 2nd Edition, India, Elsevier India, [December 1, 2015]
4. JOHN FEEHALLY, JÜRGEN FLOEGE, MARCELLO TONELLI, RICHARD J. JOHNSON, Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, Sixth Edition, Edinburgh, London, New York, Oxford, Philadelphia, StLouis, Sydney, Elsevier, [September 11, 2018]
5. VALERIE C. SCANLON, TINA SANDERS, Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, fifth edition, New York, F. A. Davis Company, [January 1, 2006]
6. KIM E. BARRETT, SUSAN M. BARMAN, HEDDWEN L. BROOKS, JASON YUAN, Ganong's Review of Medical Physiology, 26th edition, New York, Chicago, San Francisco, Athens, London, Madrid, Mexico City, Milan, New Delhi, Singapore, Sydney, Toronto, Mc Graw Hill Education, [January 29, 2019]
7. ANNE WAUGH, ALLISON GRANT, Ross and Wilson ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY in Health and Illness, 11th edition, Edinburgh, London, New York, Oxford, Philadelphia, St Louis Sydney, Toronto, Churchill Livingstone, [September 7, 2010]
The Renal tubule is a long, complicated tubule, about 15 mm long and 55 μm in diameter. The tubular portion of the nephron is the continuation of...

Urine formation happens in three major steps, The first step is glomerular filtration, which is followed by the tubular reabsorption and the tubular secretion. Click here to read about these steps in detail.

The urethra is a muscular canal that extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior of body. Read more about the anatomy of urethra in this article.

Dosage guide of Lisinopril: Click to read about the dose for your specific condition and age group.

Learn about medical uses, safety profile, mechanisms and interactions of statins.

Comprehensive guide on Ozempic (semaglutide), including its uses, dosage, side effects, warnings, and interactions.
.png)