Kidney stones are solid masses of crystals which tend to form inside the kidneys, their constituents include minerals and salts. Stones can also form in the ureters, bladder, and urethra.
While nephrolithiasis refers to stones inside the kidneys, Urolithiasis are stones that tend to originate anywhere in the urinary system (including the kidneys, both ureters, bladder, and urethra).
If you are a person with a kidney stone, you are not alone; it is estimated that 10% of all people tend to have a kidney stone at some point in their lives. Since the condition seems to be quite common, let's dive in to get more details about it!

The most common symptom people associate with having kidney stones is intense pain in the back and flank. The pain occurs as the stone passes through the ureter; thus, it stimulates nerve endings that result in experiencing pain.
Passing a kidney stone is considered to be one of the most painful conditions someone can experience; some patients tend to describe the pain they experience as an unbearable pain that comes at irregular intervals (intermittent).
Some other symptoms include:
Stones that are located in the middle part of the ureter can produce symptoms of other diseases.
For example, if the stone is on the right side, it can imitate abdominal pain of appendicitis; if it is on the left side, it can imitate abdominal pain of diverticulitis (infection of diverticula, which commonly happens on the left side).
When the kidney stone finally approaches the bladder, it manifests bladder symptoms such as urinary frequency, Painful urination (dysuria), pain in the lower abdomen, and urinary incontinence.
Generally speaking, Kidneys stones are formed when the concentration of certain types of substances {like calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), potassium (K), oxalate (CO -2), uric acid and phosphate (PO4-3)} build up. Urine naturally contains these substances, but these substances can aggregate and form crystals when their concentration gets too high (or if urine becomes too acidic or basic).
There are a couple of causes that increase the likelihood of stone formation:
(Note: only in very rare cases some stones can result from genetic disorders or certain medications)
If the situation is left unaddressed, these small crystals tend to gradually grow over time, thus forming a larger stone that can cause discomfort and the intense pain that is associated with kidney stones.
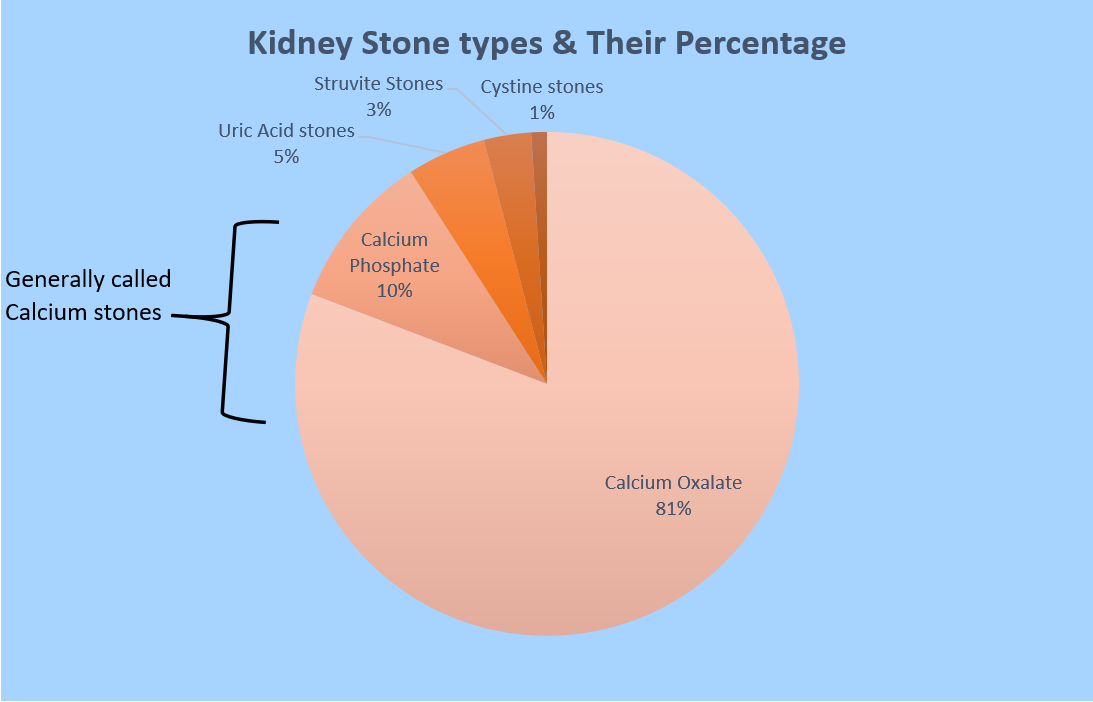
There are 4 main types of stones:
To read part 2, click here.
1. Karl Skorecki, Glenn M. Chertow et al., Brenner & Rector's the Kidney, 10th edition, Philadelphia, United States of America, Elsevier, [2016]
2. John Feehally et al., Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology, 6th edition, Philadelphia, United States of America, Elsevier -Health Sciences Division, [2018]
3. Christopher S. Wilcom et al., Therapy in Nephrology and Hypertension- A Companion to Brenner & Rector's The Kidney, 3rd Edition, Philadelphia, United States of America, Saunders/an imprint of Elsevier, [2008]
Correct diagnosis of a kidney stone has magnificent importance for the treatment and prevention of kidney stones.
.jpg)
An infection of the urinary system is called UTI, Symptoms of UTI vary according to the part of the urinary tract that is infected,

The urethra is a muscular canal that extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior of body. Read more about the anatomy of urethra in this article.

Dosage guide of Lisinopril: Click to read about the dose for your specific condition and age group.

Learn about medical uses, safety profile, mechanisms and interactions of statins.

Comprehensive guide on Ozempic (semaglutide), including its uses, dosage, side effects, warnings, and interactions.
.png)