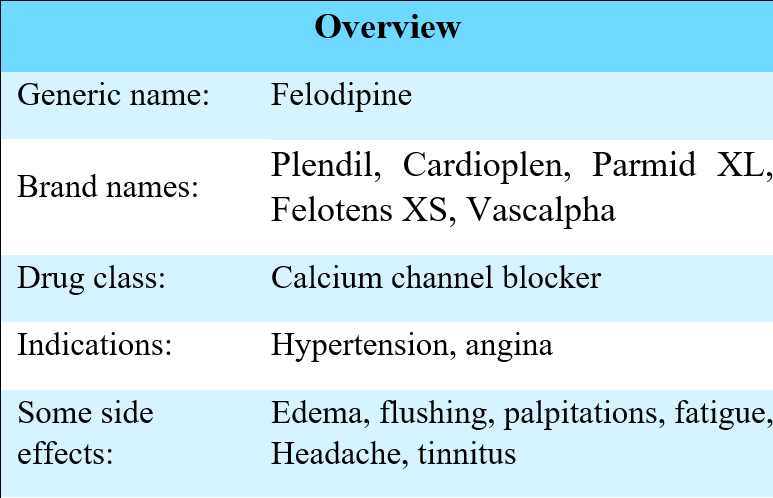
Brand name: Plendil
Felodipine is a calcium channel blocker that is used to treat high blood pressure in adults and elderly; It could be used alone or with other antihypertensive medications such as diuretics or ACE inhibitors.
Felodipine could also be used alone or with a beta blocker as a prophylaxis (prevention) for angina. The drug is available as extended-release tablets with the dosage strengths of 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg.
Uses of felodipine:
Felodipine could be taken with or without food.
You should avoid breaking, crushing, dissolving or dividing the extended-release tablets as they should be swallowed whole.
Do not stop taking felodipine without consultation with your doctor. If you stop taking felodipine abruptly you might worsen the underlying disease.
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If the time of your next dose is close by the time you remember you should take the dose which comes after it according to the schedule; However, you should not take any extra doses to make up for the missed dose.
Felodipine is not suitable for those individuals who have hypersensitivity to felodipine or other calcium channel blockers.
Felodipine is also not recommended for infants and children due to unestablished safety.
You should also inform your doctor if you are taking any other medication to avoid interactions or other undesired consequences.
Avoid taking Felodipine during pregnancy. The toxicity of felodipine during pregnancy has been confirmed in animal studies and it might cause defects in the unborn baby. There’s also a possibility that the drug may inhibit labor.
Felodipine passes into breast milk in small amounts, probably too small to cause harm. However, breastfeeding is still not recommended in order to eliminate the small chance of adverse effects on the baby.
Avoid such activities until you find out how felodipine affects you because the drug could make you dizzy and light-headed.
It’s recommended to avoid drinking alcohol. Alcohol may cause dizziness by lowering blood pressure.
Alcohol might also increase the dizziness that may result from using the drug. In addition, alcohol might enhance the blood-pressure-decreasing effect of Felodipine, especially at the beginning of the treatment.
The most common side effects of Felodipine are:
On very rare occasions, you might have a severe allergic reaction to this medication; If this occurs, you should stop taking felodipine and seek medical attention immediately.
Several drugs and other substances (such as food) can interact with Felodipine, resulting in undesired consequences.
Interaction can affect activity of Felodipine or increase the likelihood and severity of side effects, hence it’s recommended to avoid substances that interact with this medication.
Felodipine can form drug-drug interactions with these drugs:
You should not take Felodipine with grapefruit juice or other grapefruit products. Grapefruit might increase the absorption of the drug, thus having a role in producing toxic effects of the drug. Grapefruit products might also decrease the breakdown of felodipine, hence increasing both its concentration and its effects.
1. Kizior, R.J. and Hodgson, B.B. (2018). Saunders nursing drug handbook 2019. Philadelphia: Saunders.
2. British Medical Association (2015). British Medical Association new guide to medicine & drugs. London: Dorling Kindersley.
3. Joint formulary committee, BNF 80 (The British National Formulary), 80th Revised edition, Pharmaceutical Press, London, United Kingdom, [2020]
4. Baker, E., Burrage, D., Hitchings, A. and Dagan Lonsdale (2019). The top 100 drugs: clinical pharmacology and practical prescribing. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier
5. Carol Mattson Porth et al., Essentials of Pathophysiology Concepts of Altered Health States, Third edition, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States, Wolters Kluwer Health, [2011]
6. Bertam G. Katzung et al., Katzung and Trevor's pharmacology, 12th edition, United States of AmericaMcGraw Hill Education, [2019]
7. Williams and Wolters Kluwer Health (2012). Nursing 2012 drug handbook. Philadelphia, Pa.: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker and it is widely prescribed to treat high blood pressure. Read more about its other uses and side effects.
Isoptin (Verapamil) is a prescription drug used to treat high blood pressure, angina and several other problems associated with the heart.
The urethra is a muscular canal that extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior of body. Read more about the anatomy of urethra in this article.

Dosage guide of Lisinopril: Click to read about the dose for your specific condition and age group.

Learn about medical uses, safety profile, mechanisms and interactions of statins.

Comprehensive guide on Ozempic (semaglutide), including its uses, dosage, side effects, warnings, and interactions.
.png)