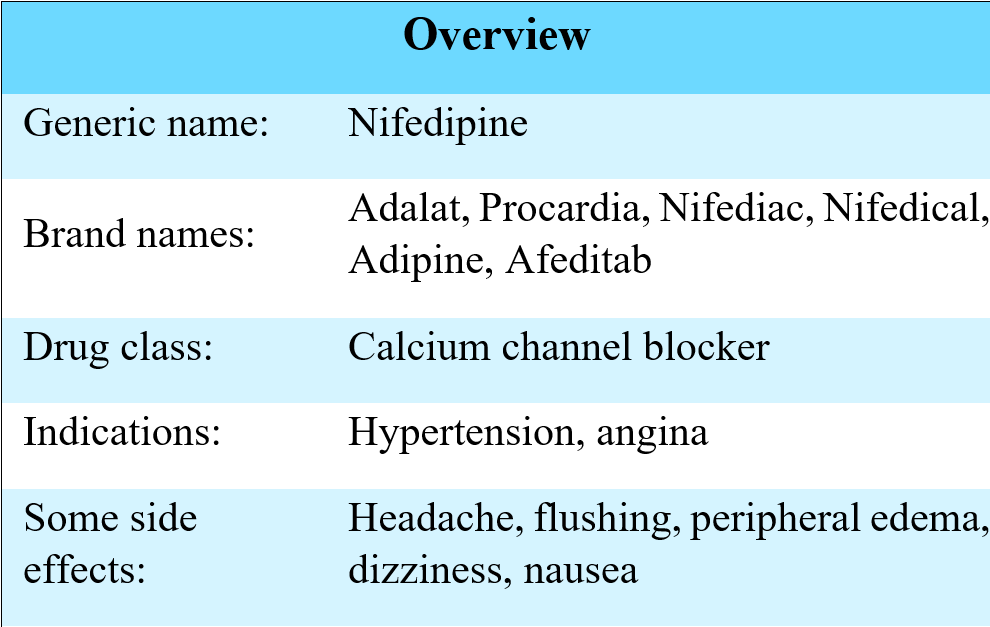
Brand names: Procardia, Adalat
Nifedipine is a prescription medicine which belongs to a class of drugs known as calcium channel blockers; it is widely prescribed to treat high blood pressure. This medication is also used in the treatment of Raynaud’s disease and angina.
Similar to other drugs of its class, it might cause hypotension and heart rhythm disturbances.
Nifedipine is used in the treatment of:
Off label uses:
Nifedipine is available as:
Avoid breaking, dissolving, dividing or crushing extended-release tablets.
Most brands of nifedipine could be taken without regards to meals. Nevertheless, some brands such as Adalat CC and Nidediac CC should only be taken on empty stomach.
If you are taking nifedipine sublingually, you should puncture, chew or squeeze the capsule in order to release the capsule’s contents into your mouth.
Do not stop taking the drug without consultation with your doctor. If you stop using the drug abruptly it may lead to worsening angina.
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember or when it’s needed, however, if you are supposed your next dose within 3 hours, take a single dose only and skip the next dose.
Make sure to tell your doctor if:
Nifedipine might inhibit labor and it has a small risk to the baby. Nifedipine is prescribed during pregnancy only if the risk to the mother with uncontrolled hypertension outweighs the risk to the baby. It’s best to discuss the matter with your doctor.
Nifedipine might affect breastfed babies since the drug passes into the milk, although some sources state that the amount is too small to cause harm. Discussing with your doctor before breastfeeding is necessary.
Nifedipine & pregnancy (detailed article)
Nifedipine causes dizziness due to its blood-pressure lowering effect; therefore, it’s recommended to avoid such activities until you have learnt how nifedipine affects you.
Avoid drinking alcohol. Alcohol may cause dizziness by lowering blood pressure.
Nifedipine is not suitable those individuals who:
The most common side effects of the drug are:
The frequency of the above side effects is between 6% to 30% in individuals who use nifedipine.
Some rare side effects of nifedipine include: rash, increased urination frequency, and increased angina. Stop taking the drug if you experience increased angina and inform your doctor as soon as possible.
On very rare occasions, you might have a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to this drug; If this occurs, you should stop taking nifedipine immediately and get immediate medical attention.
Nifedipine side effects in detail.
Nifedipine could react with many drugs and other substances resulting in production of undesired effects. Interaction can impact the activity of nifedipine or increase the likelihood and severity of its side effects.
Nifedipine can form drug-drug interactions with the following drugs:
Ginseng, garlic, yohimbe and ephedra might worsen hypertension by increasing blood pressure.
St. John’s wort decreases both the effects and the concentration of nifedipine.
Licorice might cause retention of sodium ions and water; it may also have a role in increasing the loss of potassium ions.
Grapefruit interacts with nifedipine and affects the risk of its side effects. Grapefruit products might increase the risk of headache, flushing, tachycardia and blood-pressure-lowering.
1. Kizior, R.J. and Hodgson, B.B. (2018). Saunders nursing drug handbook 2019. Philadelphia: Saunders.
2. British Medical Association (2015). British Medical Association new guide to medicine & drugs. London: Dorling Kindersley.
3. Joint formulary committee, BNF 80 (The British National Formulary), 80th Revised edition, Pharmaceutical Press, London, United Kingdom, [2020]
4. Baker, E., Burrage, D., Hitchings, A. and Dagan Lonsdale (2019). The top 100 drugs: clinical pharmacology and practical prescribing. 2nd ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier
5. Carol Mattson Porth et al., Essentials of Pathophysiology Concepts of Altered Health States, Third edition, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States, Wolters Kluwer Health, [2011]
6. Bertam G. Katzung et al., Katzung and Trevor's pharmacology, 12th edition, United States of AmericaMcGraw Hill Education, [2019]
7. Kolesar, J.M. (2017). Mcgraw-hill’s 2018/2019 top 300 pharmacy drug cards.
Felodipine is a calcium channel blocker that is used to treat high blood pressure, it could also be as a prophylaxis for angina. Read more to find out how to use this medication and learn about its side effects.
Isoptin (Verapamil) is a prescription drug used to treat high blood pressure, angina and several other problems associated with the heart.
The urethra is a muscular canal that extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior of body. Read more about the anatomy of urethra in this article.

Dosage guide of Lisinopril: Click to read about the dose for your specific condition and age group.

Learn about medical uses, safety profile, mechanisms and interactions of statins.

Comprehensive guide on Ozempic (semaglutide), including its uses, dosage, side effects, warnings, and interactions.
.png)