The urethra is a muscular canal that extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior of body. Read more about the anatomy of urethra in this article.

The ureters are tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Urinary bladder is a muscular sac that temporarily stores urine.

Micturition is the mechanism by which the urinary bladder is emptied when it becomes filled. Read about the higher centers that control micturition in this article.

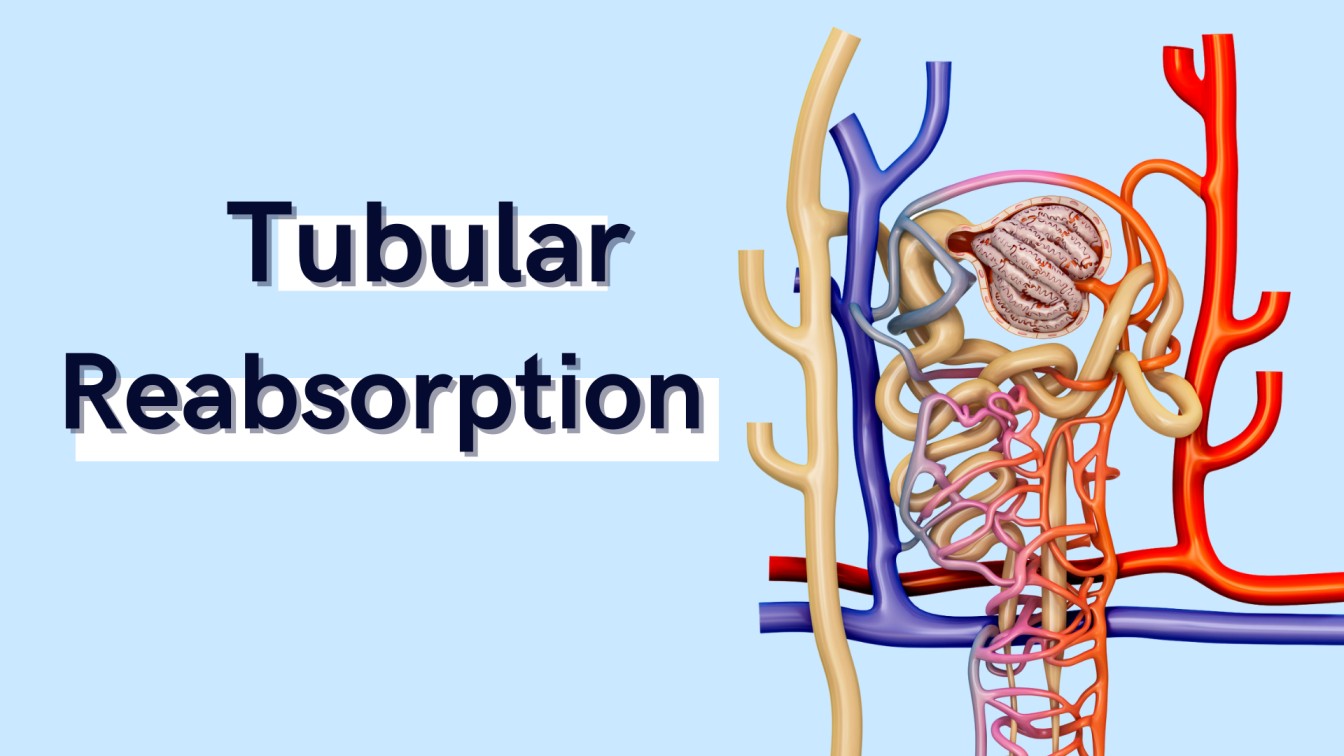
Tubular reabsorption is the mechanism by which water and other substances are transferred back to the blood from the renal tubules. Read about the mechanisms of reabsorption as well as the site at which it happens.
The glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is defined as the total amount of filtrate produced in all nephrons of both kidneys in the given unit of time.

Urine formation happens in three major steps, The first step is glomerular filtration, which is followed by the tubular reabsorption and the tubular secretion. Click here to read about these steps in detail.
