The combination of Fosinopril and hydrochlorothiazide is used in the treatment of high blood pressure (hypertension). Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic, and Fosinopril is from a class of drugs called ACE inhibitors, which is a class of drugs that work by inhibiting the production of angiotensin II, which causes vasoconstriction. As a result, Fosinopril increases the diameter of the blood vessels and improves blood flow.
| Generic name | Fosinopril and hydrochlorothiazide |
| Brand name | Monopril-HCT |
| Drug class | ACE inhibitors and diuretic |
| Drug group | Antihypertensive |
| Indications | Treatment of hypertension |
| Boxed warnings | Pregnancy |
Fosinopril/ Hydrochlorothiazide combination is available as tablets, and it is sold under the brand name: Monopril-HCT
Oral tablets
Monopril-HCT (Fosinopril-Hydrochlorothiazide)
10-12.5mg
20-12.5mg
Fosinopril hctz is used in the treatment of patients with hypertension.
Adults
Initial dose:
Fosinopril 10 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg
Fosinopril 20 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 12.5 mg
With further increase of the dose depending on the clinical response.

Elderly
No dosage adjustment is needed
Children and Infants
Safety and efficacy have not been established in pediatric patients.
Renal Impairment
1.) If creatinine clearance is ≥ 30 mL/minute: No dosage adjustment is needed.
2.) If creatinine clearance is ˂ 30 mL/minute, or serum creatinine is ≥ 3mg/dL: the combination is not recommended to be used.
Before using Fosinopril hydrochlorothiazide be cautious regarding these points:
Allergy
You should tell your doctor if you have a hydrochlorothiazide or sulfonamide-derived drugs allergy. If you are allergic to Fosinopril, or any other ACE inhibitors, or if you have had angioedema from previous treatment with ACE inhibitors.
Pregnancy
ACE inhibitors may cause injury and death to the developing fetus, especially when they are used during second and third trimesters, they should be discontinued as soon as possible once pregnancy is detected.
Breastfeeding
This drug can enter breast milk, it is contraindicated during breastfeeding.
Infants and children
The safety and efficacy of Monopril-HCT have not been established in pediatric patients.
Surgery and general anesthetics
This drug should be stopped before you have a general anesthetic. The use of ACE inhibitors will inhibit angiotensin II formation and may result in hypotension. You have to discuss it with your doctor before any operation including dental surgery.
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other drug, to reduce the risk of drug interactions.
Fosinopril hydrochlorothiazide side effects include:
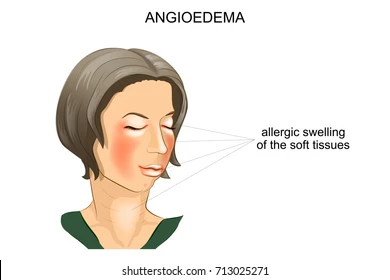


- Hyperkalemia
- Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylactic reactions)

- Syncope (fainting)
These side effects can be serious, if you experience any of them you should seek medical attention immediately.
| Drug entity | Nature of interaction |
| ACE Inhibitors |
Thiazide diuretics enhance the hypotensive effect of ACE Inhibitors. Thiazide diuretics enhance the nephrotoxic effect of ACE Inhibitors. |
| Allopurinol | Thiazide diuretics increase the possibility of allergic reactions to Allopurinol. |
| Amifostine | Antihypertensives can enhance the hypotensive effect of Amifostine.Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers |
| Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers | These can enhance the adverse effects of ACE inhibitors. |
| Antacids | Antacids decrease the serum concentration of ACE inhibitors. |
| Aprotinin | This diminishes the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. |
| Azathioprine | ACE inhibitors enhance the neutropenic effect of Azathioprine. |
| Bile acid sequestrants | Decrease the absorption of thiazide diuretics. |
| Calcitriol | Thiazide diuretics enhance the hypercalcemic effect of Calcitriol. |
| Calcium salts | Thiazide diuretics decrease the excretion of Calcium Salts. Concomitant use can also lead to metabolic alkalosis. |
| Corticosteroids | Can increase the hypokalemic effect of thiazide diuretics. |
| Cyclosporin | ACE inhibitors can enhance the nephrotoxic effect of Cyclosporin. |
| Eplerenone | Enhance the hyperkalemic effect of ACE inhibitors. |
| Ferric Gluconate | ACE inhibitors may enhance the adverse or toxic effects of ferric gluconate. |
| Lithium |
ACE inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Lithium. Thiazide diuretics may decrease the excretion of Lithium |
| Drug entity(ies) | Nature of interaction |
| Loop Diuretics |
Loop Diuretics enhance the hypotensive effect of ACE inhibitors. Loop Diuretics may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of ACE Inhibitors. |
| Methylphenidate | May diminish the antihypertensive effect of antihypertensives. |
| Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
Diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE Inhibitors Diminish the therapeutic effect of Thiazide Diuretics |
| Potassium Salts | Can enhance the hyperkalemic effect of ACE inhibitors |
| Potassium-Sparing Diuretics | May enhance the hyperkalemic effect of ACE inhibitors |
| Rituximab | Antihypertensives may enhance the hypotensive effect of rituximab. |
| Salicylates | May diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE Inhibitors |
| Sirolimus | Can enhance the adverse/toxic effect of ACE inhibitors |
| Temsirolimus | Enhances the adverse or toxic effects of ACE inhibitors. |
| Trimethoprim | May enhance the hyperkalemic effect of ACE Inhibitors. |
| Ephedra, yohimbe and ginseng | May worsen hypertension. |
| Garlic | May have increased antihypertensive effects of this combination |
1. Amy Morrison Karch (2013). 2014 Lippincott’s nursing drug guide. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
2. Lacy, C. (2006). Lexi-Comp’s Drug information handbook international. Hudson, Ohio: Lexi-Comp.
Click to read more about how the correct use of the medication, the special precautions that must be considered, as well as its side effects and interactions of fosinopril.

The urethra is a muscular canal that extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior of body. Read more about the anatomy of urethra in this article.

Dosage guide of Lisinopril: Click to read about the dose for your specific condition and age group.

Learn about medical uses, safety profile, mechanisms and interactions of statins.

Comprehensive guide on Ozempic (semaglutide), including its uses, dosage, side effects, warnings, and interactions.
.png)