Fosinopril (Monopril) is an antihypertensive agent that belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors.) It is used in the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure.
| Generic name | Fosinopril |
| Brand name | Monopril |
| Drug class | ACE inhibitors |
| Drug group | Antihypertensive |
| Boxed warnings | Pregnancy |
Fosinopril sodium acts by preventing the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II (a potent vasoconstrictor), and thus, decreases blood pressure.
Fosinopril is available as the brand name Monopril, it is available as tablets.
Fosinopril, like all of the ACE inhibitors, exerts its effect by interfering with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Fosinopril (Monopril) is a competitive ACE inhibitor, it works by preventing the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II (a potent vasoconstrictor), causing relaxation of muscles surrounding the blood vessels and dilating them, and thereby improving blood flow. It also decreases serum aldosterone, leading to decreased sodium retention, and hence, it lowers blood pressure.
This drug is absorbed slowly from the GI tract, it is metabolized in the liver and is converted to Fosinoprilat. The onset of action of Fosinopril is one hour, and its half-life is 11.5 hours.
Fosinopril is used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents in the treatment of hypertension in adults and children who weigh more than 50 kg (110 lb.).
Fosinopril is also used in the treatment of heart failure.
Fosinopril (Monopril) is available as:
Oral tablets:10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg.
Hypertension
Adults & Elderly
Initial dose: 10 mg once daily.
Maintenance dose: 20-40 mg once daily.
Maximum: 80 mg once daily.
Children (6 years and older, weighing more than 50kg)
Initial dose: 5–10 mg once daily.
Maximum dose: 40 mg once daily.
Heart failure (HF)
Adults & Elderly
Initial dose: 5-10 mg once daily, may increase the dose over several weeks.
TMaintenance dose: 20-40 mg once daily.
Maximum dose: 40 mg once daily.
Dosage in renal impairment
Reducing the dose to 5 mg in patients with heart failure is necessary.
Hepatic impairment
No dose adjustment is needed.
- Fosinopril tablets may be crushed, and taken once daily without considering meals.
- The doctor may advise you to reduce salt intake and avoid salt substitutes.
- You should not take a potassium salt supplement without consulting your doctor.
- Women of childbearing age should notify their doctor once pregnancy occurs because the drug should be stopped during pregnancy.
- Be careful, do not confuse Fosinopril with lisinopril, or Monopril with Accupril, Minoxidil, Moexipril, Monurol or Ramipril.
- Store the medication at 25°C (77°F), it should be kept in a tightly closed bottle to be protected from moisture.
Fosinopril is contraindicated in patients having allergies toward the drug or to other ACE inhibitors. Before using the drug, you should tell your doctor if have had angioedema from previous treatment with ACE inhibitors.
It should be used with caution in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function. These patients should notify their doctor before using the drug.
Diabetic patients should avoid concomitant use of Fosinopril with Aliskiren (a direct renin inhibitor).
Fosinopril should be used with caution in patients having aortic stenosis, collagen vascular disease, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and renal artery stenosis.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Fosinopril is not prescribed during pregnancy and breastfeeding, because it can cross the placenta and distribute in breast milk, so it may cause harm and death to the developing fetus.
Children and infants
Safety and efficacy have not been established. Neonates and infants are at increased risk for oliguria and neurologic abnormalities.
Surgery and general anesthetics
This drug should be stopped before you have a general anesthetic. The use of ACE-inhibitors will inhibit angiotensin II formation and may result in hypotension.
You have to discuss it with your doctor before undergoing any operation (including dental surgery).
Fosinopril may cause a variety of side effects, mainly dizziness and cough
Less common side effects of Fosinopril may include:



- Hypotension
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Palpitation
- Hyperkalemia
- Musculoskeletal pain
- Visual impairment
- Urinary disorder
- Edema (swelling of tongue, lips, face, eyes, arms, or legs)
- Sexual dysfunction
You should notify your prescriber if you experience any of these side effects.
If you take more than the recommended amount of Fosinopril, you may experience serious and harmful symptoms of Fosinopril overdose. In case of an overdose, you should immediately notify your doctor.
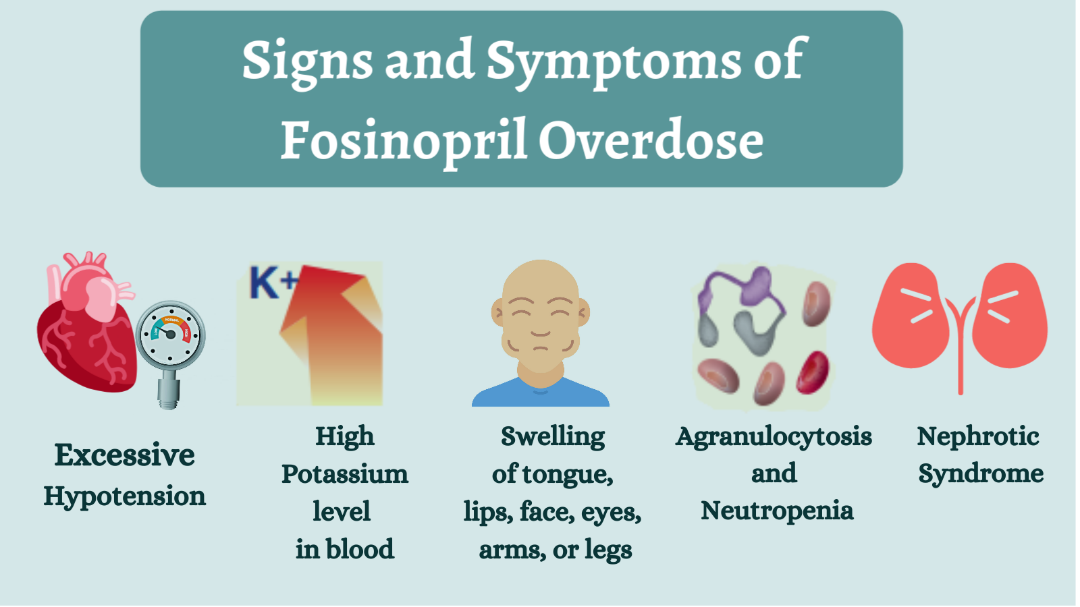
Toxic reactions of Fosinopril (Monopril) may include:
Excessive hypotension may occur in patients with heart failure which might lead to fainting after the first dose ("first-dose syncope").
Angioedema (swelling of face and lips).
Hyperkalemia (high potassium level in blood) may occur in rare cases.
Agranulocytosis and neutropenia might be noted in patients with renal impairment and collagen vascular disease.
Nephrotic syndrome can be noted in patients with a history of renal disease.
NO
Several drugs and substances can interact with Fosinopril resulting in undesired effects. Interaction can affect the activity of the drug or increase the severity of the side effects.
Fosinopril sodium can form drug-drug interactions with the following drugs:
| Drug entity | Nature of interaction |
| Azathioprine | Increase risk of anemia or leukopenia. |
| Alcohol, diuretics and antihypertensive agents | Increase the blood pressure-lowering effect (cause excessive hypotension). |
| Potassium supplements, potassium-sparing diuretics & Ciclosporin | Increase the risk of hyperkalemia. |
| Antacids | May decrease the absorption. |
| Lithium | Blood levels of lithium are raised by Fosinopril. May lead to lithium toxicity. |
Drug-herb interactions
Capsaicin may cause cough. Therefore, concomitant use with Fosinopril should be avoided.
Ma-huang decreases the antihypertensive effects of Fosinopril.
Ephedra, ginseng and yohimbe can worsen hypertension, hence may interact with this medication.
Garlic increases the antihypertensive effect of Fosinopril.
Licorice can cause sodium & water retention, and loss of potassium.
Drug-food interactions
1. Kizior, R.J. and Hodgson, B.B. (2018). Saunders nursing drug handbook 2019. Philadelphia: Saunders.
2. Lacy, C. (2006). Lexi-Comp’s Drug information handbook international. Hudson, Ohio: Lexi-Comp.
3. Joint formulary committee, BNF 80 (The British National Formulary), 80th Revised edition, Pharmaceutical Press, London, United Kingdom, [2020]
4. Williams and Wolters Kluwer Health (2012). Nursing 2012 drug handbook. Philadelphia, Pa.: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
ACE inhibitors are a class of drugs that are used in the treatment and management of high blood pressure and heart failure. Find a list of ACE inhibitors in this article.

The urethra is a muscular canal that extends from the neck of the bladder to the exterior of body. Read more about the anatomy of urethra in this article.

Dosage guide of Lisinopril: Click to read about the dose for your specific condition and age group.

Learn about medical uses, safety profile, mechanisms and interactions of statins.

Comprehensive guide on Ozempic (semaglutide), including its uses, dosage, side effects, warnings, and interactions.
.png)